Developer Guide
- Acknowledgements
- Setting up, getting started
- Design
- Implementation
ResumeWindowis opened or reopened to show the current values.- Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
- Appendix: Requirements
- Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
- { more test cases … }
- Appendix: Planned Enhancements
Acknowledgements
- {list here sources of all reused/adapted ideas, code, documentation, and third-party libraries – include links to the original source as well}
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Design
.puml files used to create diagrams in this document docs/diagrams folder. Refer to the PlantUML Tutorial at se-edu/guides to learn how to create and edit diagrams.
Architecture
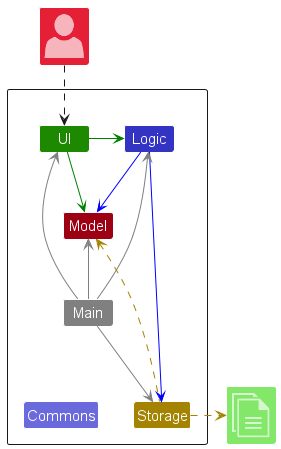
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main (consisting of classes Main and MainApp) is in charge of the app launch and shut down.
- At app launch, it initializes the other components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down, it shuts down the other components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
The bulk of the app’s work is done by the following four components:
-
UI: The UI of the App. -
Logic: The command executor. -
Model: Holds the data of the App in memory. -
Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command delete 1.
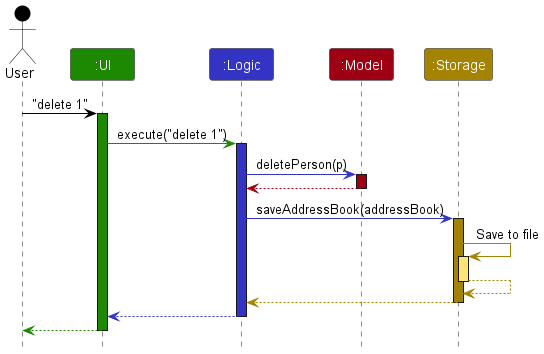
Each of the four main components (also shown in the diagram above),
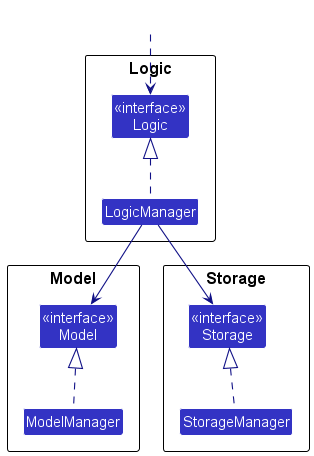
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - implements its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which follows the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
For example, the Logic component defines its API in the Logic.java interface and implements its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which follows the Logic interface. Other components interact with a given component through its interface rather than the concrete class (reason: to prevent outside component’s being coupled to the implementation of a component), as illustrated in the (partial) class diagram below.
The sections below give more details of each component.
UI component
The API of this component is specified in Ui.java
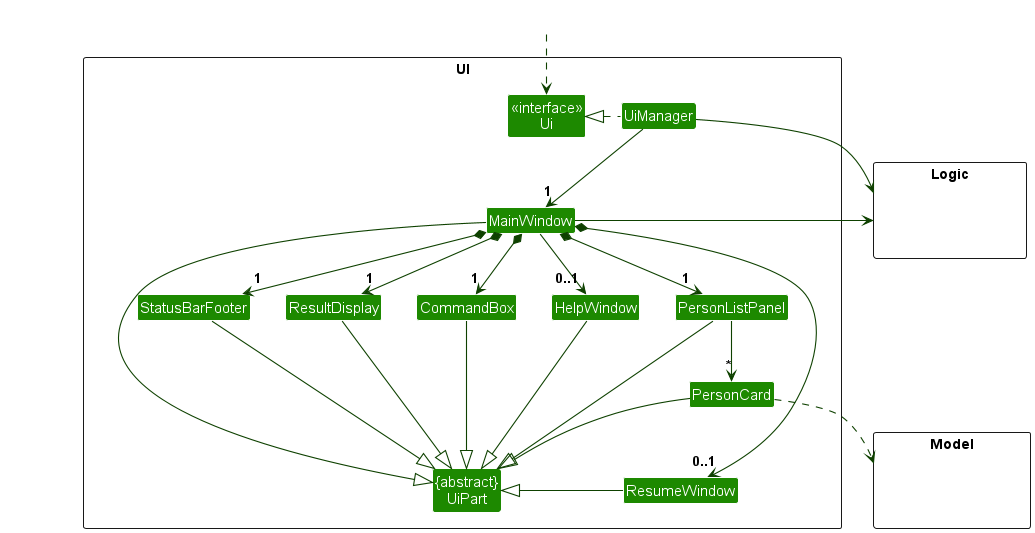
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, PersonListPanel, StatusBarFooter etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The UI component uses the JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
Logiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysPersonobject residing in theModel.
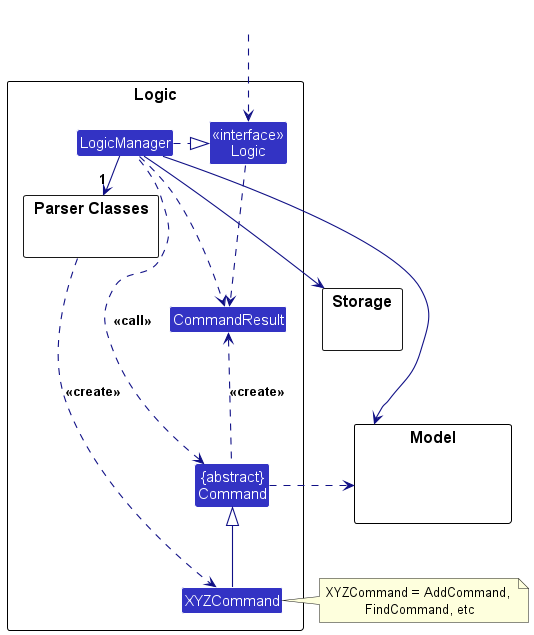
Logic component
API : Logic.java
Here’s a (partial) class diagram of the Logic component:
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component, taking execute("delete 1") API call as an example.
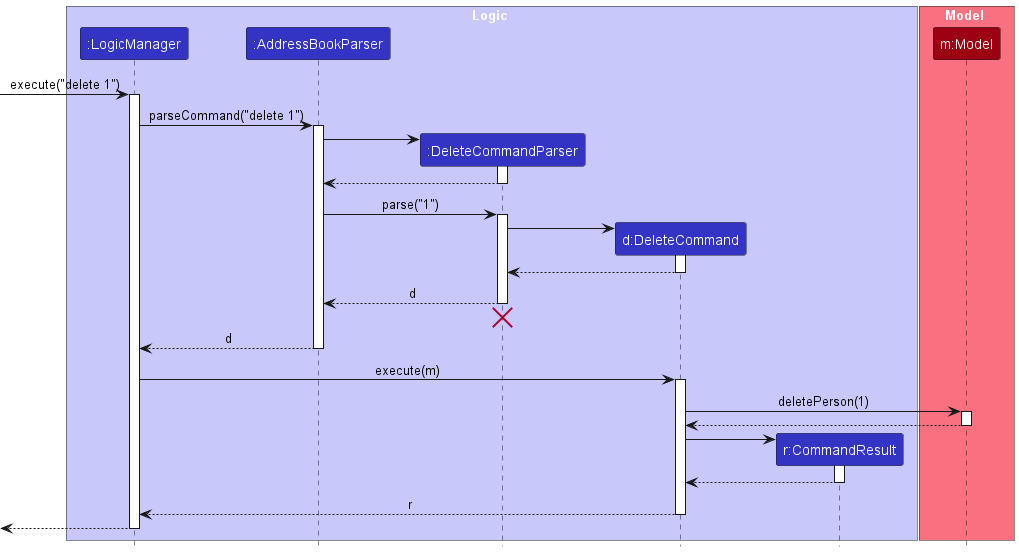
DeleteCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of diagram.
How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it is passed to anAddressBookParserobject which in turn creates a parser that matches the command (e.g.,DeleteCommandParser) and uses it to parse the command. - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses e.g.,DeleteCommand) which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command can communicate with the
Modelwhen it is executed (e.g. to delete a person).
Note that although this is shown as a single step in the diagram above (for simplicity), in the code it can take several interactions (between the command object and theModel) to achieve. - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is returned back fromLogic.
Here are the other classes in Logic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing a user command:
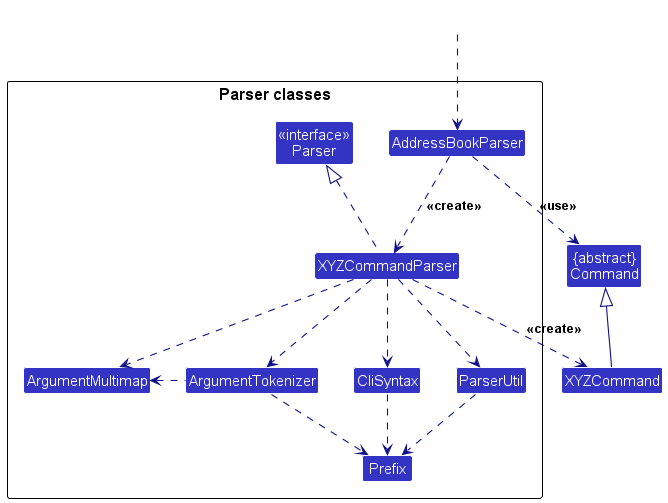
How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
AddressBookParserclass creates anXYZCommandParser(XYZis a placeholder for the specific command name e.g.,AddCommandParser) which uses the other classes shown above to parse the user command and create aXYZCommandobject (e.g.,AddCommand) which theAddressBookParserreturns back as aCommandobject. - All
XYZCommandParserclasses (e.g.,AddCommandParser,DeleteCommandParser, …) inherit from theParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing.
Model component
API : Model.java
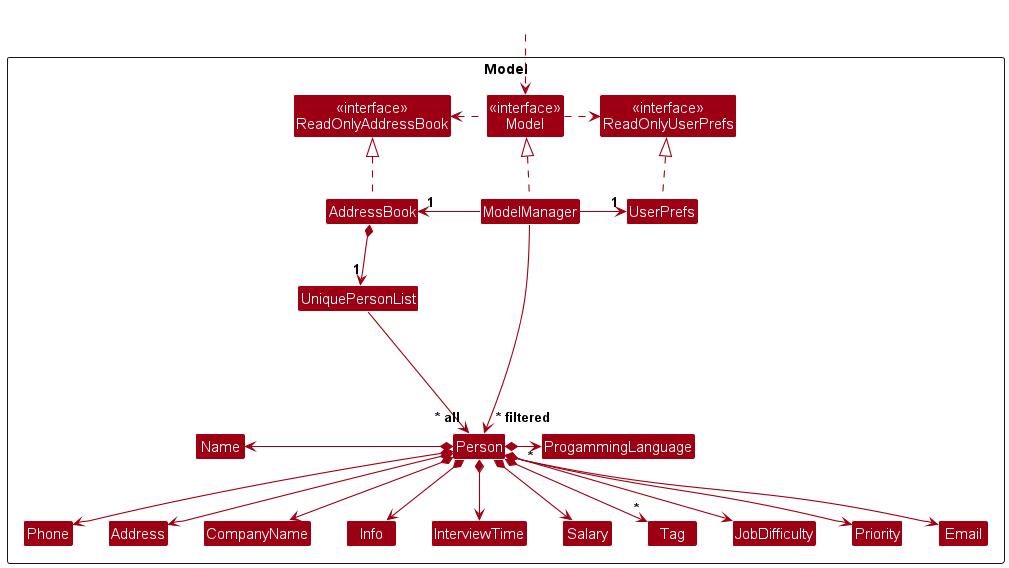
The Model component,
- stores the address book data i.e., all
Personobjects (which are contained in aUniquePersonListobject). - stores the currently ‘selected’
Personobjects (e.g., results of a search query) as a separate filtered list which is exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Person>that can be ‘observed’ e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. This is exposed to the outside as aReadOnlyUserPrefobjects. - does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
Modelrepresents data entities of the domain, they should make sense on their own without depending on other components)
Tag list in the AddressBook, which Person references. This allows AddressBook to only require one Tag object per unique tag, instead of each Person needing their own Tag objects.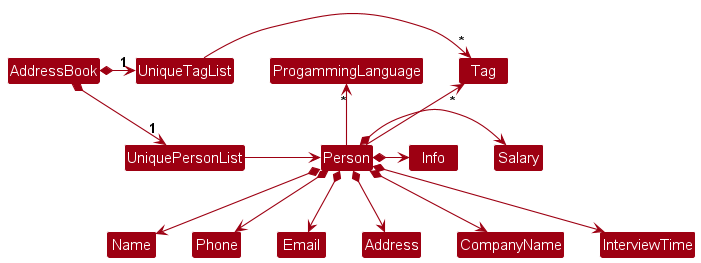
Storage component
API : Storage.java
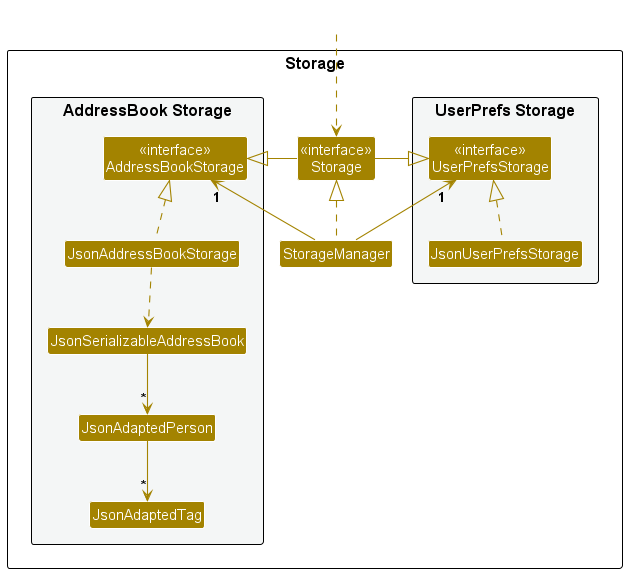
The Storage component,
- can save both address book data and user preference data in JSON format, and read them back into corresponding objects.
- inherits from both
AddressBookStorageandUserPrefStorage, which means it can be treated as either one (if only the functionality of only one is needed). - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent (because theStoragecomponent’s job is to save/retrieve objects that belong to theModel)
Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.addressbook.commons package.
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
Sorting Contact List
Overview of SortCommand
This feature allows users to sort their addressbook based on various information, namely name, company
name, interview time, salary and priority. This feature leverages on the built-in ObservableList provided by JavaFX.
The sorting is done by creating classes that implements the Comparator
Comparator Classes
PersonCompanyNameComparator.javaPersonInterviewTimeComparator.javaPersonNameComparator.javaPersonPriorityComparator.javaPersonSalaryComparator.java
These comparators are referenced in the SortCommandParser. In the SortCommandParser each comparator will be assigned
a static integer based on the CLI Syntax from the userInput. The string is that parsed and assigned an integer from
1 - 4 which are pre-assigned to a comparator.
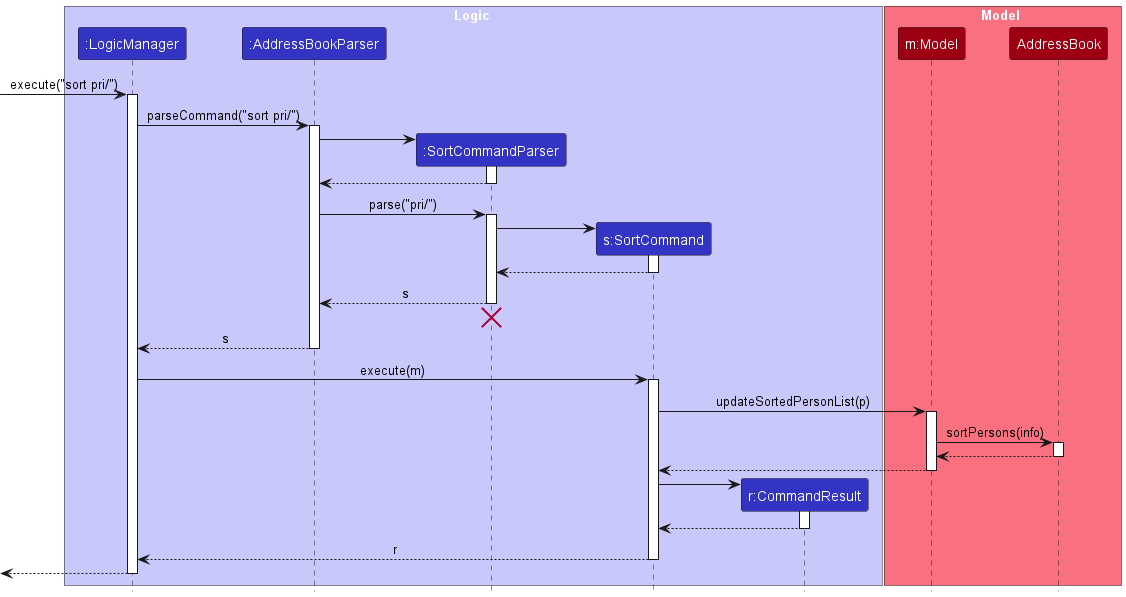
Process:
- User inputs
sort pri/, triggering theexecute()function in theLogicManagerobject.-
pri/is a CLI syntax added to refer to priority, an attribute added to thePersonclass.
-
-
LogicManagerinvokes theparseCommand()function in theAddressBookParser, which interprets thesortcommand and creates aSortCommandParserobject. - The
SortCommandParserparsespri/and creates theSortCommandobject.- The
SortCommandconstructor accepts an Integer, withSortCommandParserpre-assigningpri/to 0.
- The
-
LogicManagerexecutes the command. -
SortCommandcallsupdateSortedPersonList()from theModelobject, which references theAddressBookcontaining theUniquePersonList. TheUniquePersonListsorts based on the assigned comparator.
Class Structure
-
SortCommandclass: Responsible for executing the sort operation based on the specified attribute. Inherits from theCommandclass and utilizes multiple comparator classes to sort contacts based on various attributes.
Method Details
-
SortCommand(Integer info, boolean isInverse): Constructor that takes an integer representing the attribute index and a boolean indicating whether to sort in reverse order. -
execute(Model model): Executes the command to sort the list of contacts in the address book based on the specified attribute. Utilises switch-case statements to select the appropriate comparator and sorts the contacts accordingly. -
equals(Object other): Overrides the equals method to compare if twoSortCommandobjects are equal based on the attribute index.
Job Difficulty Feature
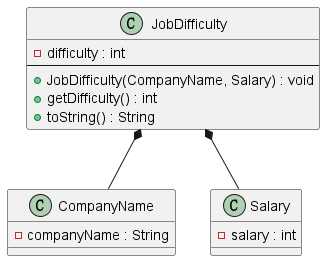
Overview of Job Difficulty Feature
The job difficulty feature calculates a difficulty score for a job based on the company name and salary. It utilises the local storage of renowned company names and their job difficulty levels.
Class Structure
-
JobDifficultyclass: Responsible for computing the job difficulty score. UtilizesCompanyNameandSalaryclasses to fetch the necessary information.
Method Details
-
JobDifficulty(CompanyName companyName, Salary salary): Constructor that takes aCompanyNameobject and aSalaryobject to compute the job difficulty score. -
getDifficulty(): Returns the calculated job difficulty score.
Filtering of List Feature
Overview of Filtering List Feature
This feature allows users to filter their lists according to the interview time range, tags, salary range and programming language.
Implementation
-
FilterCommandclass: An abstract class inherited by concrete classes, such asFilterInterviewTimeCommand,FilterTagCommand,FilterSalaryCommand, andFilterProgrammingLanguageCommand. These classes filter the list according to their respective categories.
Process:
-
FilterCommandParserdetermines a concrete subclass ofFilterCommandto return. - The concrete
FilterCommandClasschecks if their respective categories (interview times, tags, etc.) in the contact list contain the keyword. - Returns the list of contacts containing the keyword.
Deleting Contacts With Same Tag Feature
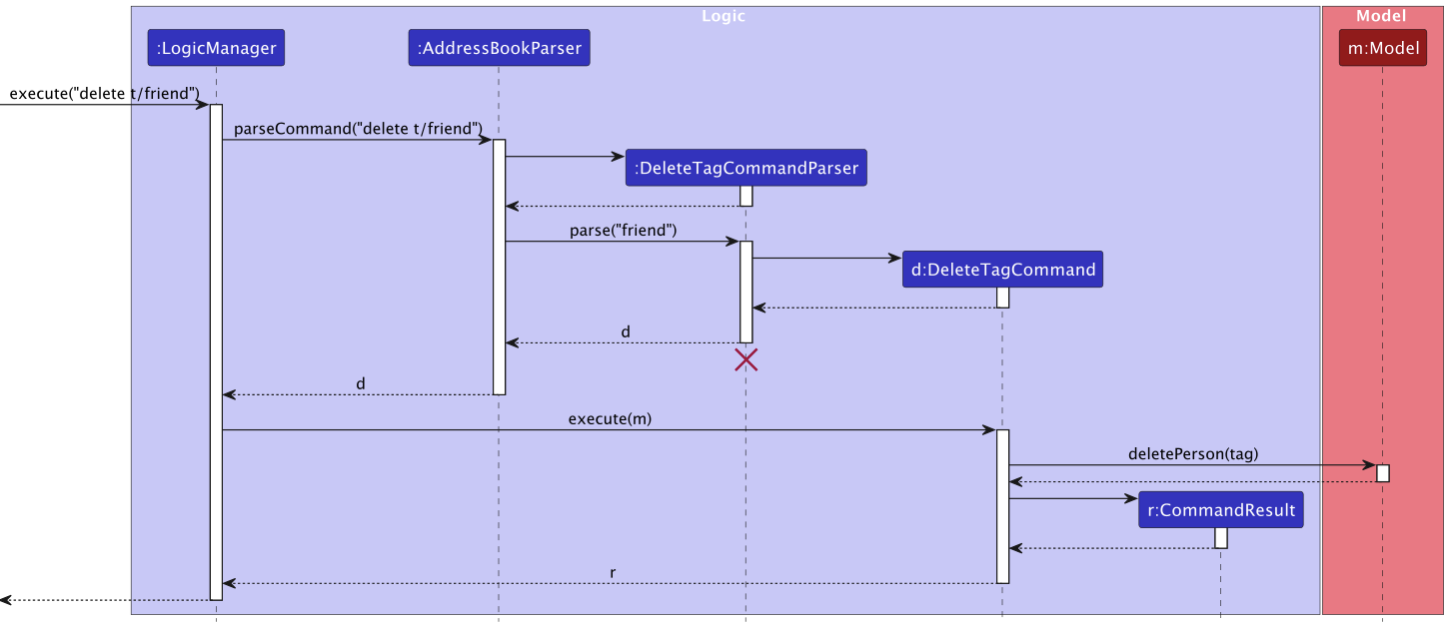
Overview of DeletingTagCommand
The DeleteTagCommand feature enables users to delete all contacts associated with a specified tag from the address
book. This feature uses the TagContainsKeywordsPredicate class to filter and identify contacts with the specified tag for deletion.
Process:
-
DeleteTagCommandParserdetermines a concrete subclass ofDeleteTagCommandto return. - The concrete
DeleteTagCommandclass retrieves the list of tags to be deleted from theTagContainsKeywordsPredicate. - Filters the contacts in the address book based on these tags.
- Deletes the filtered contacts from the address book model.
Class Structure
-
DeleteTagCommandclass: Responsible for executing the delete operation based on the specified tag. Inherits from theDeleteAbstractCommandclass and utilizes theTagContainsKeywordsPredicateclass to filter contacts.
Method Details
-
DeleteTagCommand(TagContainsKeywordsPredicate tagToDelete): Constructor that takes aTagContainsKeywordsPredicateobject representing the tag to be deleted. -
execute(Model model): Executes the command to delete all contacts with the specified tag from the address book. Retrieves the list of tags to be deleted, filters the contacts based on these tags, and deletes them from the model.
Finding Contact Name by Company Name Feature
Overview of FindCommand
The FindCommand feature allows users to search and list all persons in the address book whose name or company name
contains any of the specified keywords. This feature employs the NameOrCompanyNameContainsKeywordsPredicate class to
filter and identify contacts based on their names or company names.
Process:
-
FindCommandParserdetermines a concrete subclass ofFindCommandto return. - The concrete
FindCommandclass checks if the names or company names of contacts in the address book contain the specified keywords. - It returns the list of contacts whose names or company names contain the keyword.
Class Structure
-
FindCommandclass: Responsible for executing the find operation based on the specified keywords. Inherits from theCommandclass and utilizes theNameOrCompanyNameContainsKeywordsPredicateclass to filter contacts.
Method Details
-
FindCommand(NameOrCompanyNameContainsKeywordsPredicate predicate): Constructor that takes aNameOrCompanyNameContainsKeywordsPredicateobject representing the keywords to search for. -
execute(Model model): Executes the command to find and list all contacts whose names or company names contain the specified keywords. Retrieves the list of contacts matching the predicate, updates the filtered contact list in the model, and returns a command result indicating the number of contacts found.
Add resume feature
The add resume feature allows user to add their own personal and professional details that would be required in a
job search. This feature has its own UI, similar to the Help feature.
Implementation
This feature introduces a new User singleton class. The structure is as shown below.
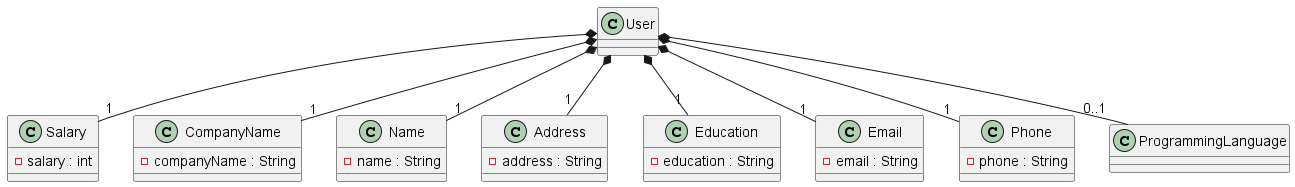 The
The ResumeWindow controller, that controls the FXML file that displays the resume, has a reference to the
User class to retrieve the values of the user, if any.
Process:
- User inputs
resume...into UI. - The
UIManagerthen callsLogicManager -
AddressBookParseris called. -
AddressBookParserresets the User’s attributes and re-assigns them to the current inputs -
AddResumeCommandis instantiated and itsexecute()is called to returnCommandResult -
ResumeWindowis opened or reopened to show the current values.
Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
- computing professionals looking for job openings
- has a need to manage a significant number of company contacts
- prefer desktop apps over other types
- can type fast
- prefers typing to mouse interactions
- is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition: User will be able to manage and schedule interview contacts, timings and job listings from a centralised location. Also manage contacts faster than a typical mouse/GUI driven app
User stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
* * * |
Computer science job seeker | delete features | delete information where necessary | |
* * * |
Computer science job seeker | add contact information of interviewer / company | contact the interviewer / company | |
* * * |
Computer science job seeker | add salary range | check the salary range of the job | |
* * * |
Computer science job seeker | add company name | check which company the job is from | |
* * * |
Computer science job seeker | add extra info about the company | recall the extra information about each of the companies | |
* * * |
Computer science job seeker | add interview time | check what is the interview time | |
* * |
Computer science job seeker | add programming language(s) related to the job | identify which programming language(s) is/are required for the job | |
* * |
Computer science job seeker | add job responsibilities | check what are the job responsibilities for the job | |
* * |
Computer science job seeker | categorise job postings according to industry | filter information based on the different types of industries | |
* |
Computer science job seeker | receive notifications when I get a new interview | stay up-to-date with the interview offers and attend them | |
* |
Computer science job seeker | track the status of my job application | follow up with any actions when necessary | |
* |
Computer science job seeker | receive reminders for my interview timings | be reminded about the interview |
Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is the AddressBook and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: Delete a person
MSS
- User requests to list persons
- AddressBook shows a list of persons
- User requests to delete a specific person in the list
-
AddressBook deletes the person
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
-
3a. The given index is invalid.
-
3a1. AddressBook shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: Add a Contact with Detailed Information
MSS
- The user decides to add a new contact to their address book.
- The user inputs the add command followed by the contact’s details in the format: add n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]….
- CCBot validates the input details.
- CCBot adds the new contact to the address book, assigning it a unique identifier within the system.
-
CCBot displays a confirmation message to the user indicating the successful addition of the new contact.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 3a. If the user enters invalid details (e.g., incorrect format, missing mandatory fields like name or phone number):
-
3a1. CCBot shows an error message indicating the validation failure and the correct format of the command.
Use case resumes at step 2. *a. At any time, User chooses to cancel the addition. *a1. CCBot requests to confirm cancellation *a2. User confirms the cancellation Use case ends. —
-
Use case: Add Salary Range to a Contact
MSS
- The user decides to add a new contact with the salary or salary range info to their address book.
- User inputs the ‘add’ command with the salary detail in the correct format.
- CCBot validates the salary format and range.
-
CCBot adds or updates the salary information for the contact and displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 3a. If the salary detail is invalid:
-
3a1. CCBot shows an error message indicating the validation failure and the correct format of the command.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: Add the Company’s Name to a Contact
MSS
- The user decides to add a new contact with the company’s name info to their address book.
- User inputs the ‘add’ command with the company’s name in the correct format.
- CCBot validates the salary format and range.
-
CCBot adds or updates the company’s name information for the contact and displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 3a. If the company’s name is bigger than 100 characters:
-
3a1. CCBot shows an error message indicating the validation failure and the limit characters number.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: Add Programming Language to a Contact
MSS
- The user decides to add a new contact with the programming language info to their address book.
- User inputs the ‘add’ command with the programming language detail in the correct format.
- CCBot validates the salary format and range.
-
CCBot adds or updates the programming language information for the contact and displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 3a. If the programming language detail is invalid:
-
3a1. CCBot shows an error message indicating the validation failure and an error message about the format or character limit.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: Add extra info about the company to a Contact
MSS
- The user decides to add a new contact with extra company info to their address book.
- User inputs the ‘add’ command with the extra information detail in the correct format.
- CCBot validates the input details.
-
CCBot adds or updates the extra information for the contact and displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 3a. If the extra information detail is invalid:
-
3a1. CCBot shows an error message indicating the validation failure and an error message about the format or character limit.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
11or above installed. - Should be able to hold up to 1000 persons without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- User Interface should be intuitive enough for users to easily add interview dates and salaries.
- System should be able to cater to various date formats given by users.
- System should be able to handle a minimum of 100 contacts
{More to be added}
Glossary
- Computer Science job seeker : Student / Unemployed / Working adult seeking employment opportunities in the field of Computer Science
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, MacOS
- Private contact detail: A contact detail that is not meant to be shared with others
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Launch and shutdown
-
Initial launch
-
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
-
Double-click the jar file Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample contacts. The window size may not be optimum.
-
-
Saving window preferences
-
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
-
Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
-
-
{ more test cases … }
Deleting a person
-
Deleting a person while all persons are being shown
-
Prerequisites: List all persons using the
listcommand. Multiple persons in the list. -
Test case:
delete 1
Expected: First contact is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted contact shown in the status message. Timestamp in the status bar is updated. -
Test case:
delete 0
Expected: No person is deleted. Error details shown in the status message. Status bar remains the same. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete x,...(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
-
{ more test cases … }
Saving data
-
Dealing with missing/corrupted data files
- {explain how to simulate a missing/corrupted file, and the expected behavior}
-
{ more test cases … }
Appendix: Planned Enhancements
Team size: 5
-
Have an error message show up when the data file is corrupted on startup: The current address book simply starts up with an empty list when the data in the json file is corrupted or has an invalid format. The current implementation has a logger warning shown in the developer console, but not the app itself. We plan have an error message show up on results display after startup of the app when the data is corrupted.
-
Allow
filtercommand to filter the contact list based on a combination of categories: The currentfiltercommand only allows the contact list to be filtered based on one specific category such as tags, salary range etc and this may not be useful for users with a very huge number of contacts as filtering by only one category may still return a long list. It is also not convenient for users who want to find contacts more specifically. We plan to allowfilterto filter the contact list more specifically. (e.g.filter t/TAG s/SALARY_RANGEwill return contacts with matchingTAGandSALARY_RANGEthat falls within what is specified) -
Show more specific error messages for our features: The current
add,edit,resume,filter,find,sort, anddeletecommand requires prefixes such ast/ands/as their parameters. This may be confusing for users as they may input the wrong prefix for a command (e.g. inputedu/inaddcommand instead of in theresumecommand). We plan to allow the error message to throw more specific errors:Invalid Command Format! edu/ is part of the resume command and not the add command. -
Improve help command functionality by making it easier for CLI users: Makes it so that the
helpcommand bring up a tab with the link to the user guide automatically highlighted. This allows the user to simply use the keyboard shortcutctrl-cto copy the link to their clipboard, instead of having to use the mouse to click the copy button manually. This allows users using the CLI to use the app more effectively. -
Allow
addcommand to add contacts with the same name: The current version of the application restricts the addition of contacts with identical names, assuming that each contact should have a unique name. However, it is not uncommon for people to have the same name, and this restriction can be limiting. We propose to enhance the application to allow multiple contacts with the same name, while ensuring that each contact is uniquely identifiable by other means such as company name, email, or phone number. The updated application will allow the addition of contacts with the same name. To differentiate between contacts with identical names, additional details such as company name, email, or phone number will be used. This approach will maintain the uniqueness of each contact within the application. Adjust the contact validation logic to check for uniqueness based on the combination of name and one or more of the additional identifying details. If a contact with the same name and other identifying details already exists, the application will prompt the user to confirm the addition of the new contact instead of adding it immediately. -
Allow
findcommand to search contact list with partial name/company name matches: The existingfindcommand focuses on exact matches for names or company names. This limitation can be restrictive, especially when users are unsure about the complete name or are looking for contacts with names that have common substrings. To provide a more flexible and intuitive search experience, we plan to enhance the find command to support partial matching. The improved find command will enable users to search for contacts using partial names or partial company names. The command will display a list of contacts where the entered term matches any part of the person’s name or company name. (e.g.find jwill return contacts with names like “John” and company names like “JPMorgan”.) -
Store the resume such that the user can retrieve it later. The existing implementation of the program does not store the user’s resume but only binds it to the current instance of the program. This can be limiting as users would have to re-input their resume everytime they open the application. Even thought it is unlikely that a resume can change as often as a contact in the addressbook. To provide a better user experience, we plan to store the resume and enable the application to read the stored resume, if any, whenever it starts.
-
Allow user to edit the resume. The existing implementation of the program, does not allow users to edit the resume. Currently, user would have to call
resumecommand and re-input the values if they want to update them. This can be limiting as it results in unnecessary inconvenience of having to re-input all the values instead of editing just the intended one. To provide a more intuitive experience, we plan to enhance theeditcommand such that users can directly access the current resume and edit the values. (e.gedit resume s/3000will update the salary on the resume to 3000) -
Allow user to store multiple versions of the resume. The existing implementation does not allow users to store multiple resumes. This can be limiting as users may want to retrieve specific versions of the resume. To make the experience more intuitive, we plan to create a separate storage system to allow users to store multiple resumes. For instance, calling the
resumecommand will create a separate resume to store, instead of overwriting the current resume. -
Ask for confirmation from users when
deleteandclearcommand is executed: The current implementation allows users to clear and delete contacts from the contact list. Users may accidentally delete important contacts or misunderstand the function of the commands. Hence, we plan to show a warning to tell them thatdeletewill cause the contact to be deleted permanently and thatclearwill clear the whole list permanently and thereafter ask for a confirmation to exceute the commands.